The Management of Mild, Moderate and Severe Oral Epithelial Dysplasia at University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire
A4
Caren Kaur Jauhal
Caren Kaur Jauhal BDS, David M McGoldrick BDS MB BCh MSc FFDRCSI (OSOM) FRCS (OMFS), Gary M Walton BDS FDSRCS MDS MSc MBChB FRCS (Eng) FRCS (OMFS)
Aim
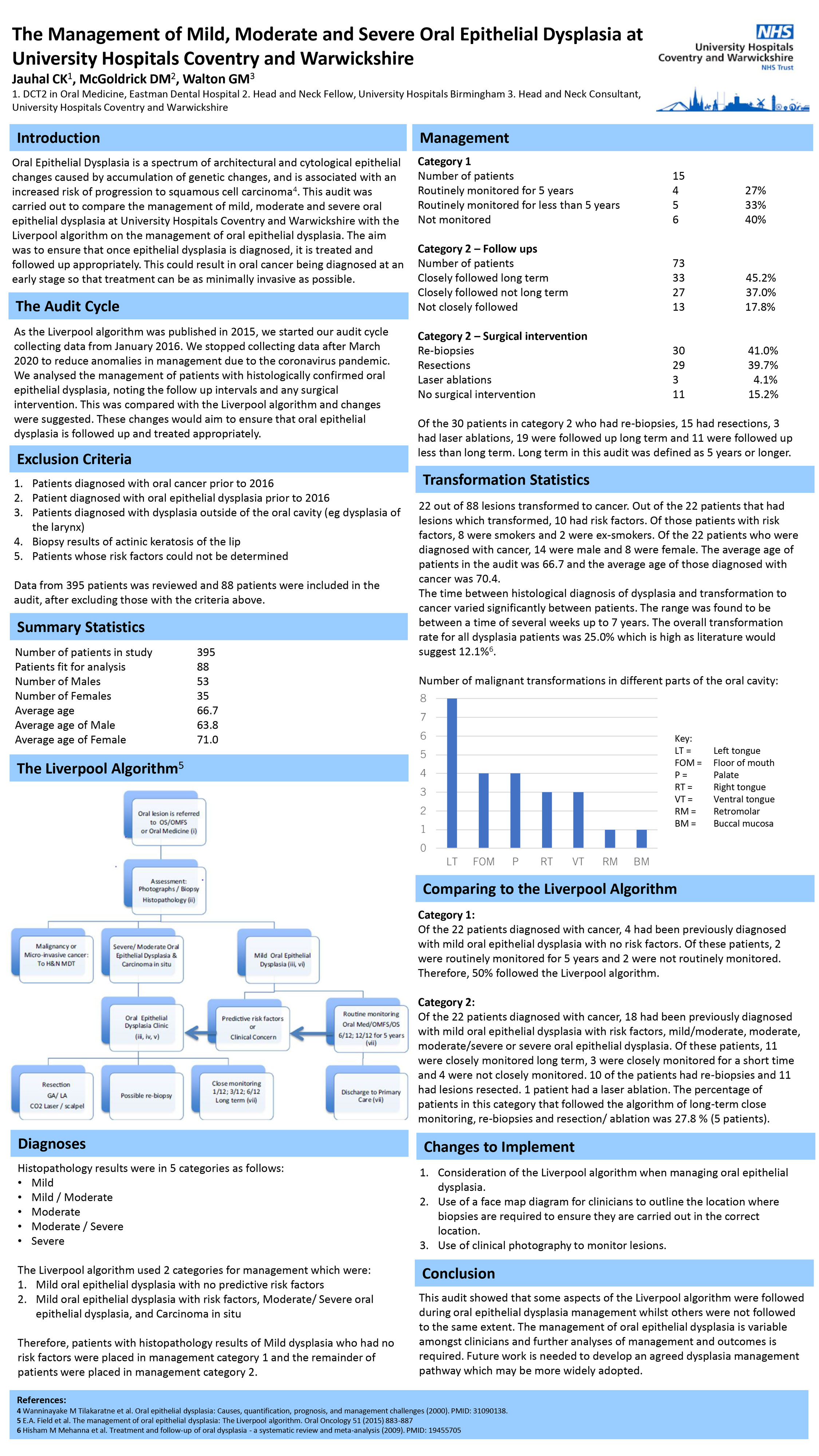
Audit on management of minor, moderate and severe oral epithelial dysplasia (OED) at UHCW, with data compared with the Liverpool algorithm for management of OED. Aim is that OED is treated and monitored appropriately so that treatment options can be as minimally invasive as possible.
Process
As the Liverpool Algorithm was published in 2015, I started my audit cycle collecting data from January 2016 until March 2020 (to reduce anomalies in management during covid-19). I assessed the biopsy results of OED, noting the follow up intervals and management techniques used. I then compared results to the Liverpool Algorithm. The data from 395 patients was reviewed and 88 patients were included in the audit after excluding those with exclusion criteria.
Histology results at UHCW are in 5 categories; Mild, Mild-Moderate, Moderate, Moderate-Severe and Severe. The Liverpool algorithm uses 2 categories for management:
1. Mild OED with no predictive risk factors
2. Mild OED with risk factors, Severe/ Moderate OED and Carcinoma in situ
Therefore, the biopsy diagnoses of Mild with no risk factors were placed in management category 1 and the remainder in management category 2.
Transformation statistics
22 out of 88 lesions transformed to cancer. The transformation rate was 25.0% which is high as literature would suggest 12.1% (Hisham M Mehanna et al, 2009).
Comparison with the Liverpool Algorithm
27.0% of patients in category 1 were routinely monitored for 5 years and 45.2% of patients in category 2 were closely monitored for 5 years. Out of the 73 patients in category 2, 30 patients had re-biopsies. Of those 30 who had re-biopsies, 15 then had resections and 3 had laser ablations.
Advised changes to implement including; consideration of the Liverpool Algorithm, use of mouth diagram to outline location where biopsies are required, use of clinical photography for monitoring purposes.